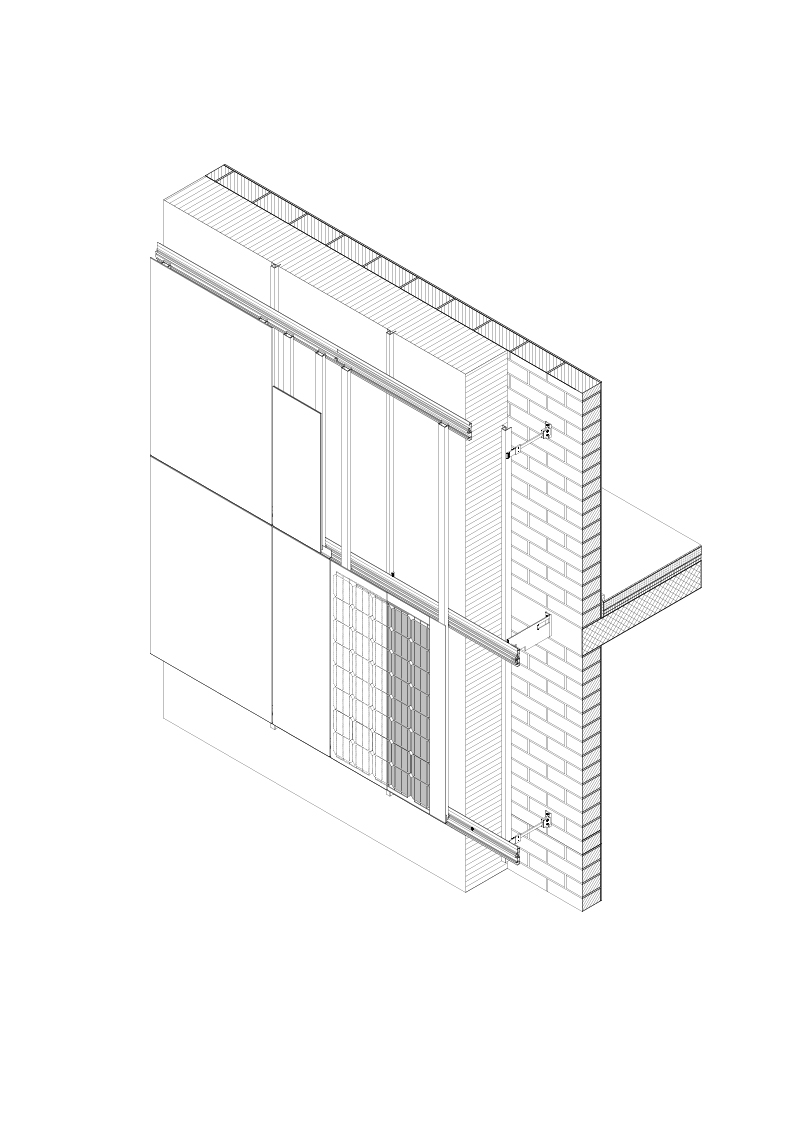
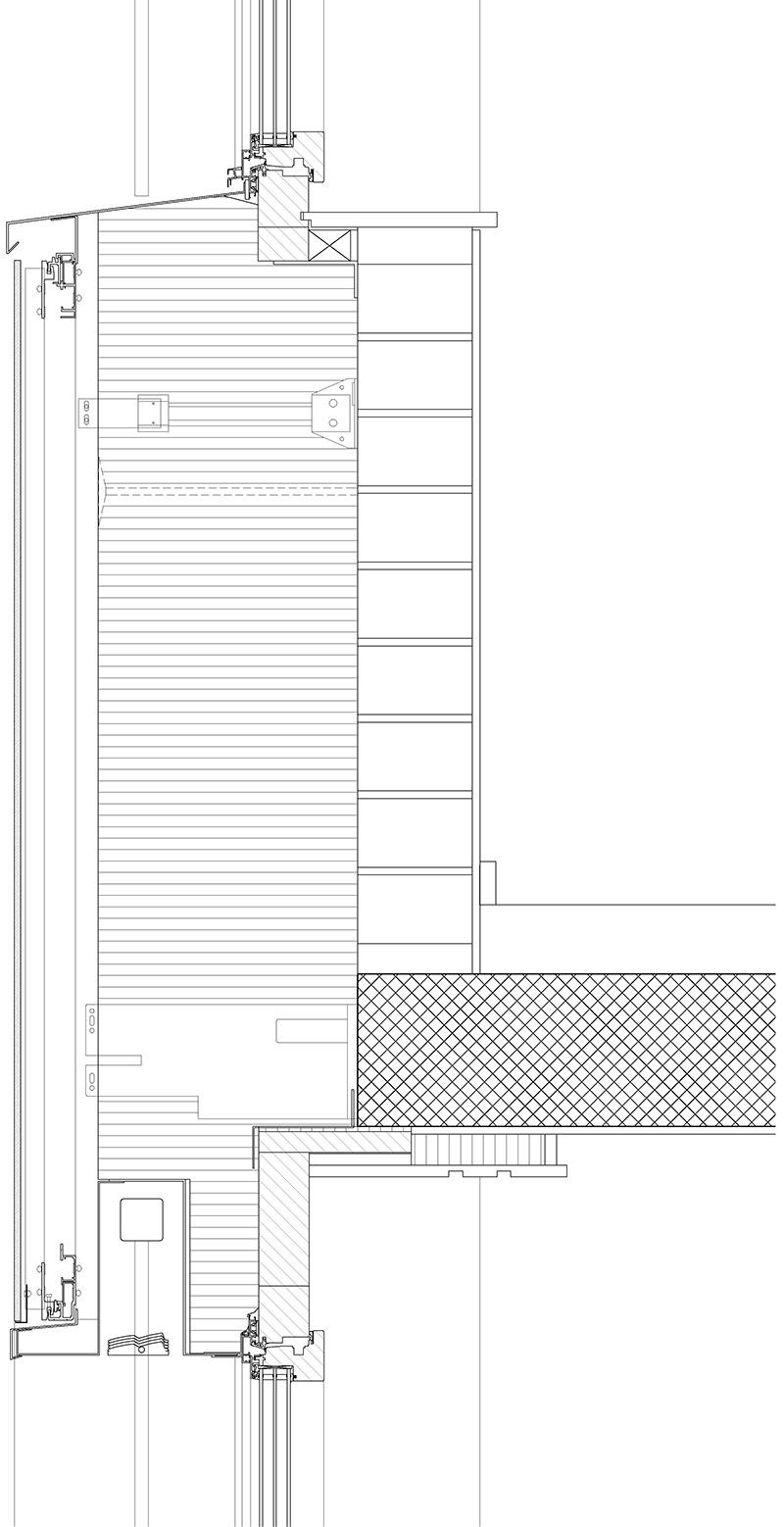
This multi-family building, built in 1982, is the result of a retrofit intervention, with a forth-floor extension, which is characterized by the change in its appearance thanks to the use of coloured photovoltaic modules which allow the facade to assume an homogeneous appearance as the “active” parts are not immediately recognizable. The PV modules have a matte surface and this causes a reduction of the solar power output by about 39% as the green/grey colour is given by the front glass.

Floor plan

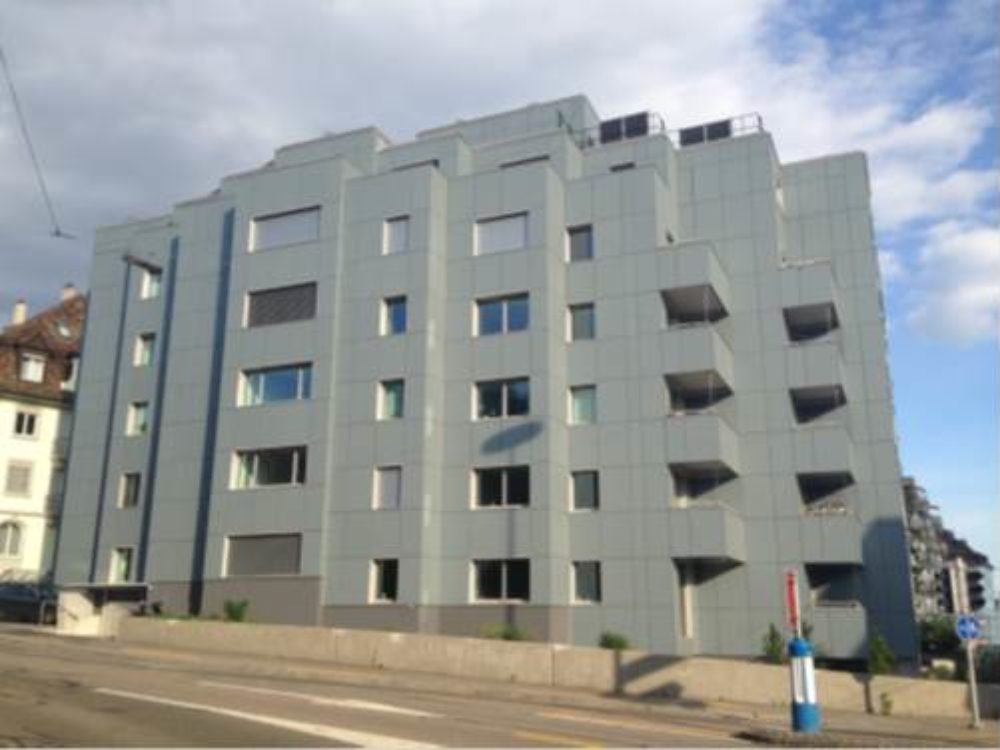
View of the building before the retrofit

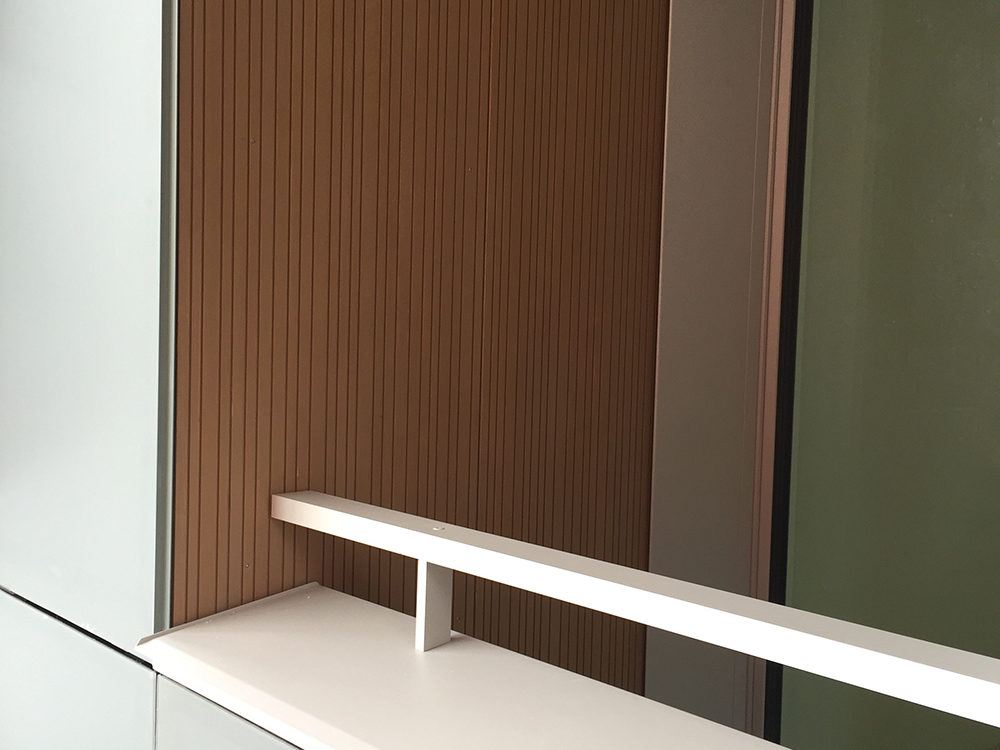
Dummy modules were used on 2% of the total surface area of the facade.
| Active solar surface | 165 m² | 1586 m² |
| Active solar surface ratio | n/a | >75% |
| Peak power | 20 kWp | 159 kWp |
| Building skin application | Flat roof | Cold facade |
| Storage | n/a | n/a |
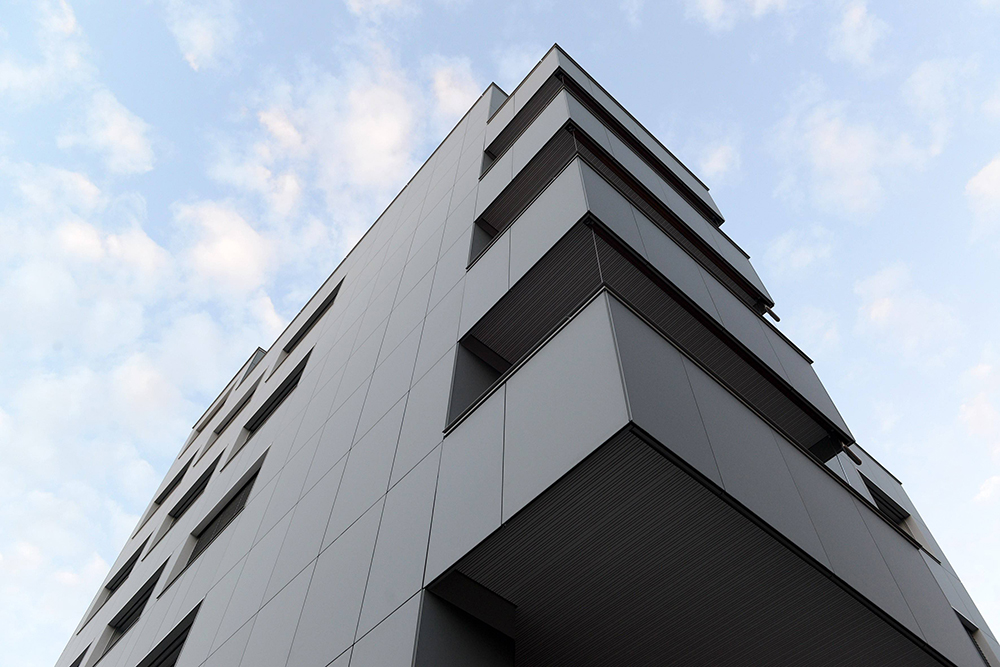

The new cladding is made of “invisible” PV modules with a matte surface.
The existing 4-storey residential building was a 2-shell masonry with an intermediate insulation of 8 cm.
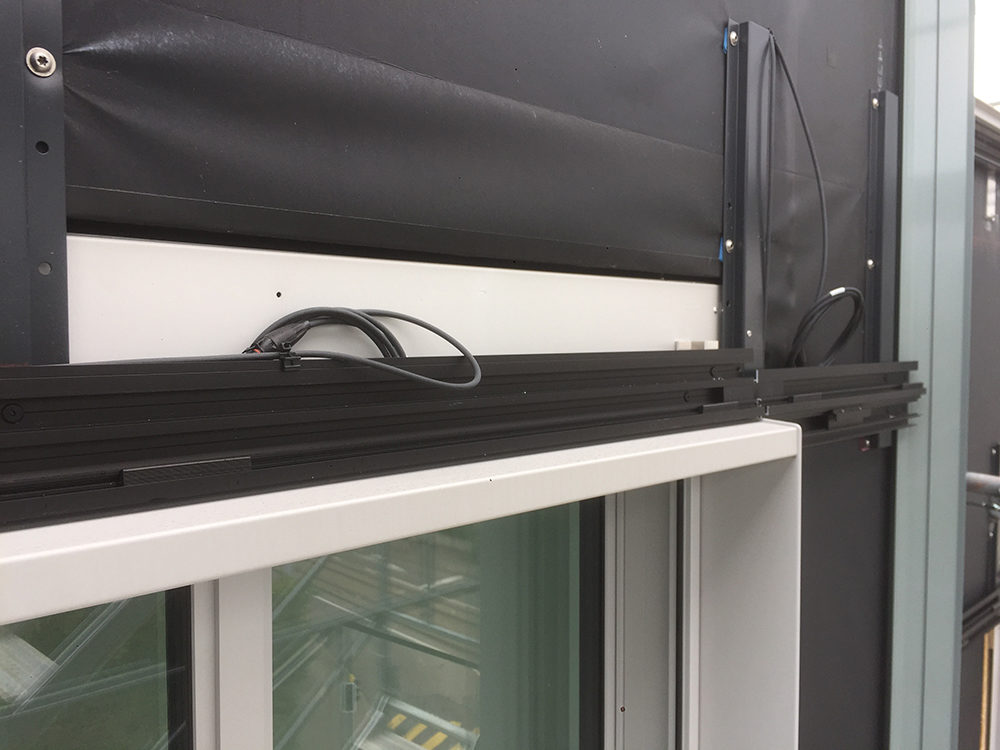
For static reasons, the perimeter wall could not fulfil the requirements of the new cold facade and was therefore completely removed. The aim of the project was to develop a building envelope, which was not only the protective, aesthetic and energetic layer but would also serve as an energy supplier.