This new residential building designed and built in Stabio has received Minergie P-ECO / SNBS certification, and a commendation at the Active House Awards 2022. It is the first building in Ticino to achieve the highest Swiss standard for sustainable construction (SNBS).
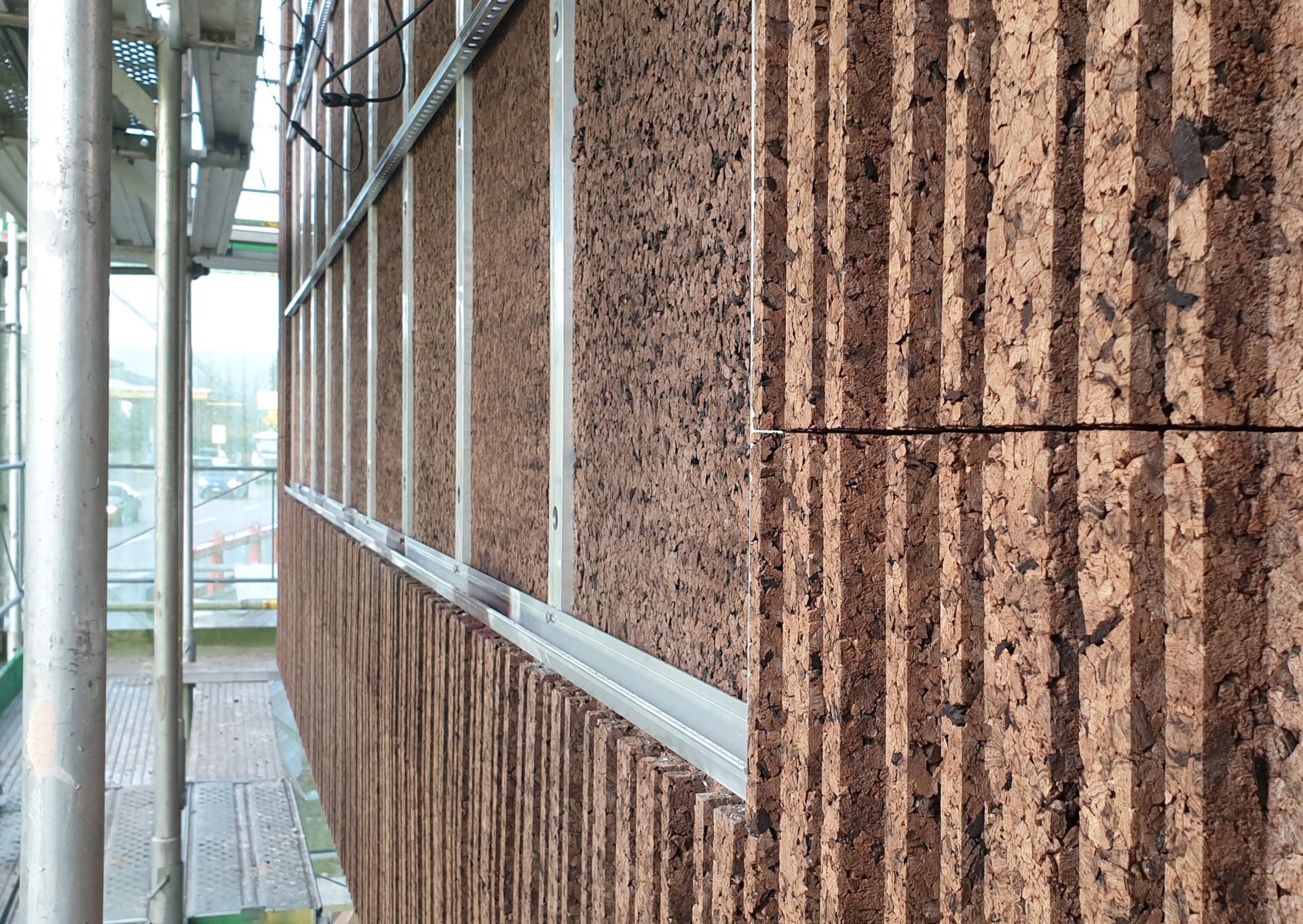
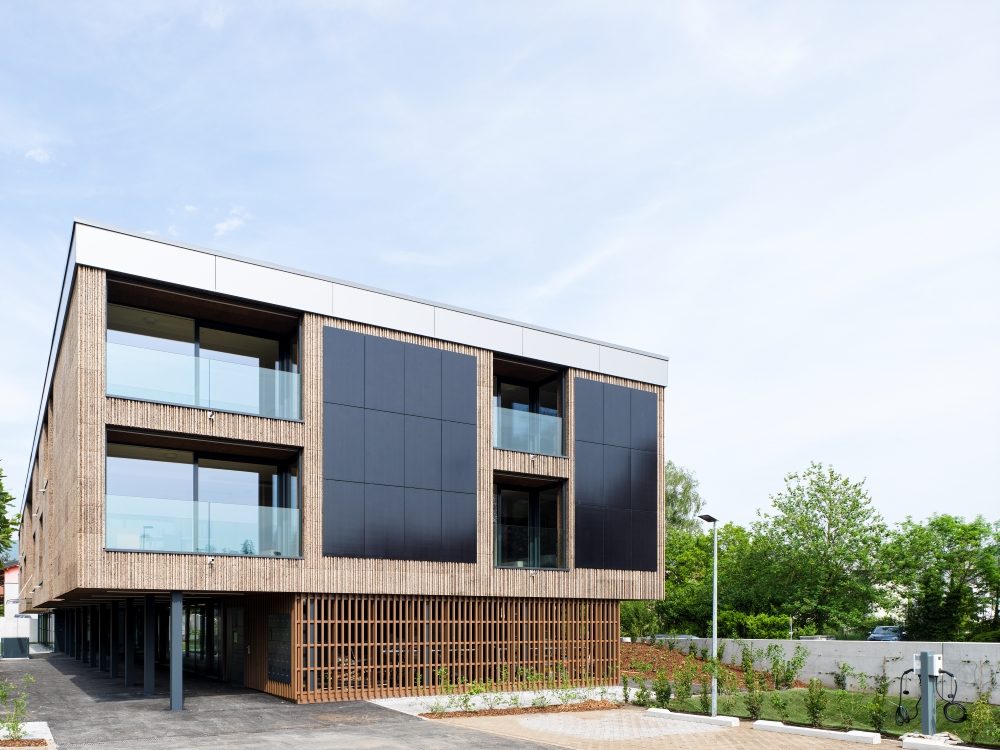
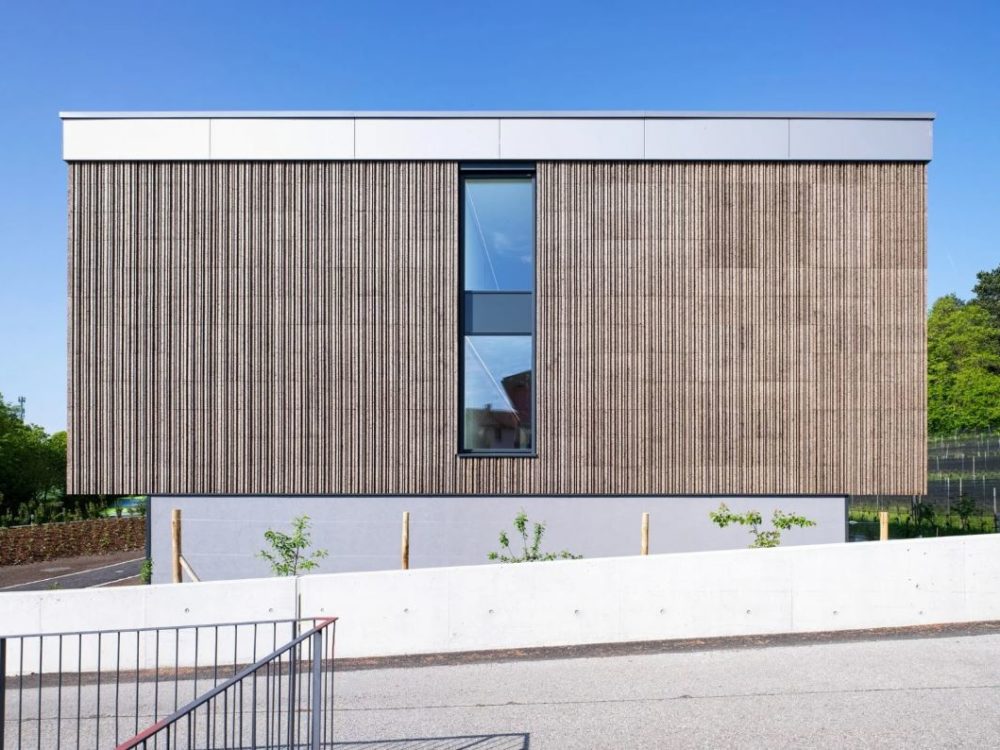
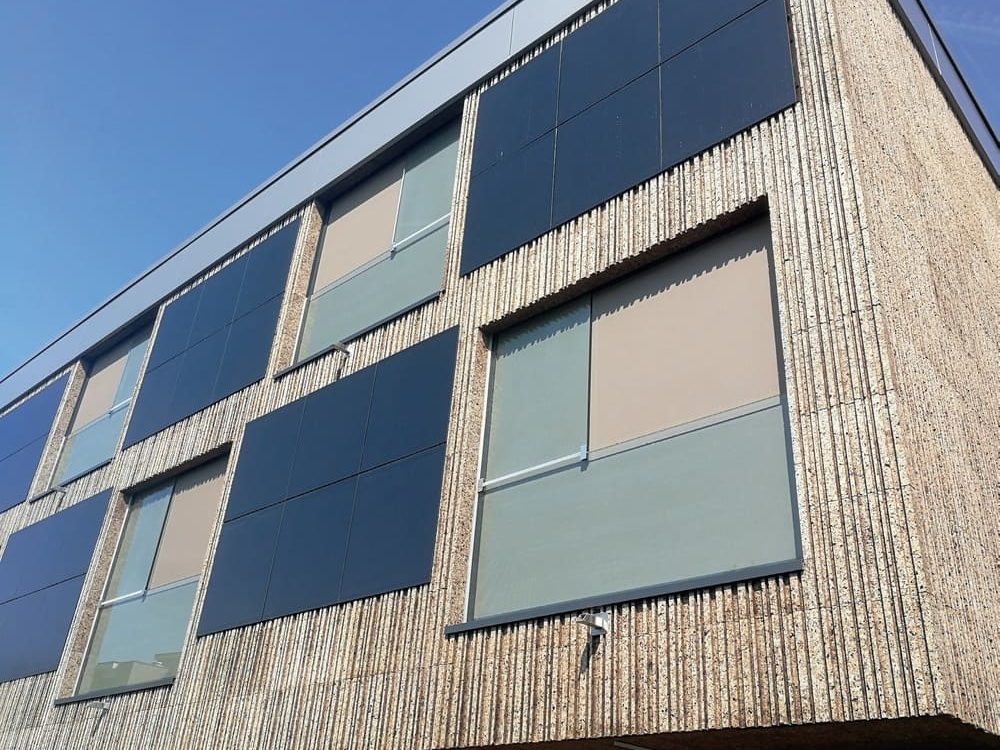
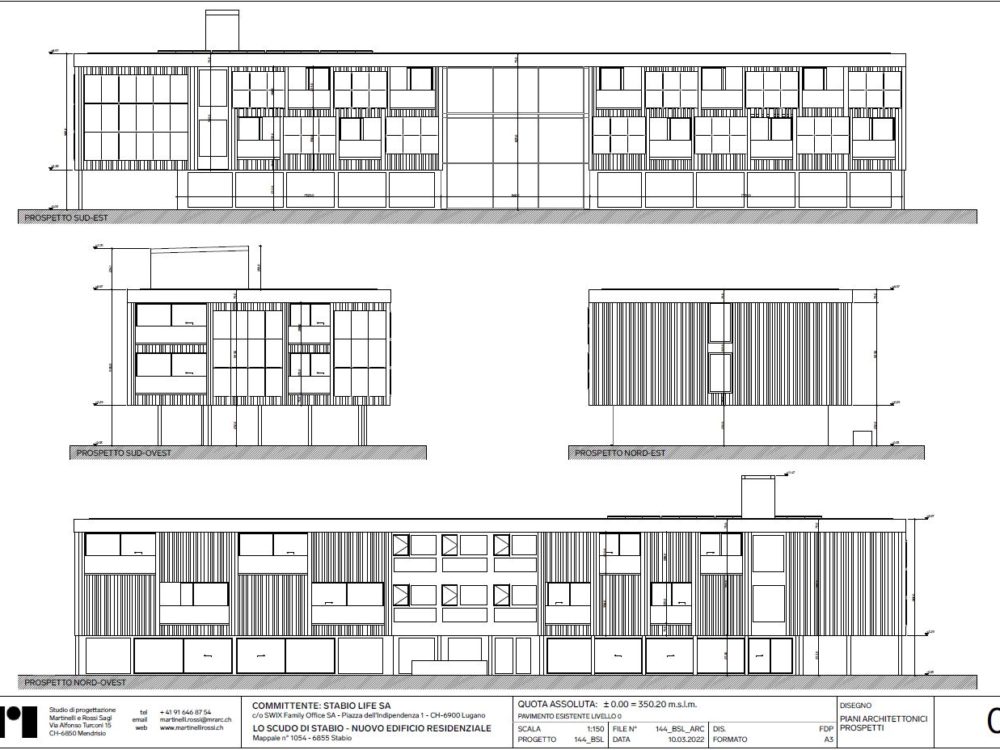
The cork facade wraps around the timber framed supporting structure. The idea behind the facade is to reconstitute a technological cortex with a motif reminiscent of the digital world of vertical barcodes interspersed with crystalline silicon photovoltaic mineral modules on the south and west facades.
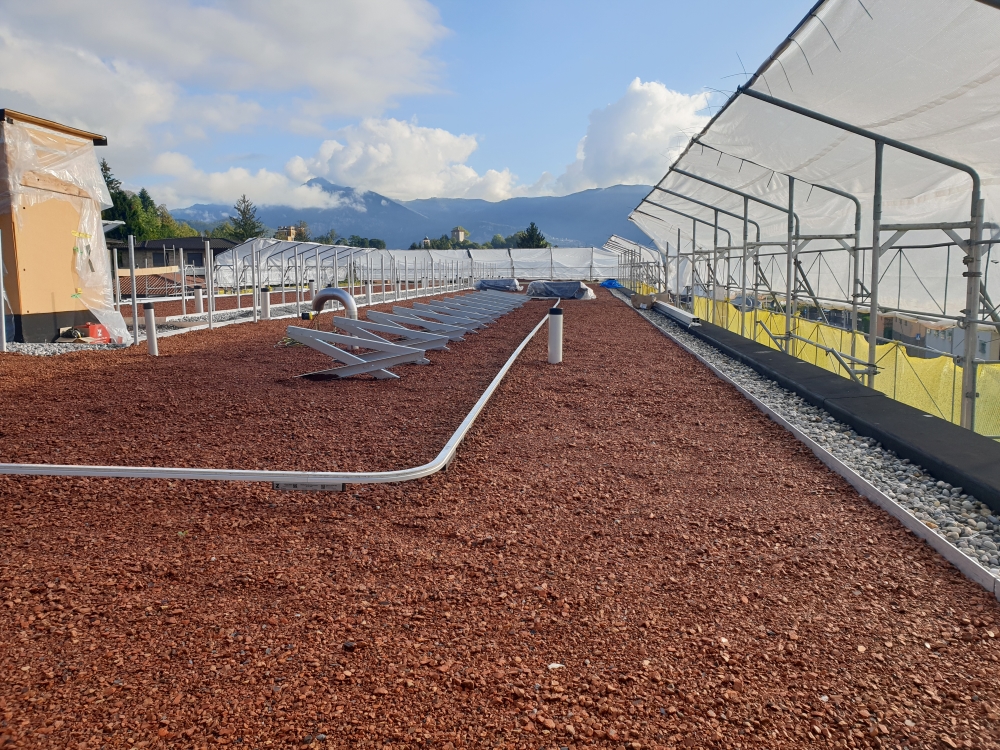
A small portion of the green roof is also occupied by additional photovoltaic modules, but without limiting the presence of extensive greenery that, together with the arrangement of the outdoor spaces, participates in the regeneration and enrichment of the biodiversity of the neighbouring context (flora and small fauna with particular attention to avian fauna).
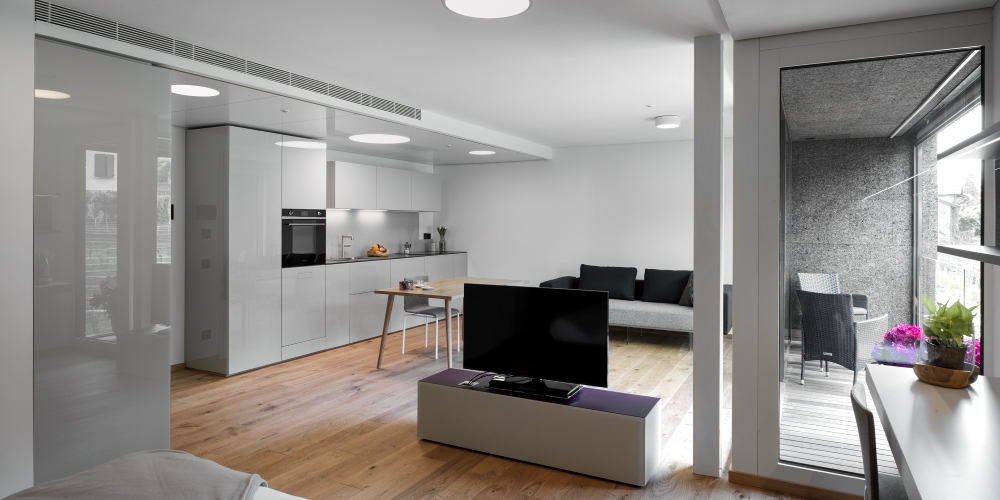
The urban planning model referred to is that of the ‘smart city’, or intelligent city, with the concretisation of community housing models according to the latest ‘smart living’ and ‘co-working’ methods. In this case, a residential ‘hub’ was designed for short-term rentals: a building halfway between a multi-family residence and a hotel structure. Twenty-two fully furnished flats, ready to be inhabited even for a few weeks, and equipped with a Konnex KNX standard for home automation in the service of sustainability.
The building also promotes electric mobility with recharging stations for cars, and provides tenants with electric bicycles, which, together with new-generation storage batteries installed in the technology rooms, allow 100% self-consumption of the energy produced by the photovoltaic installation.
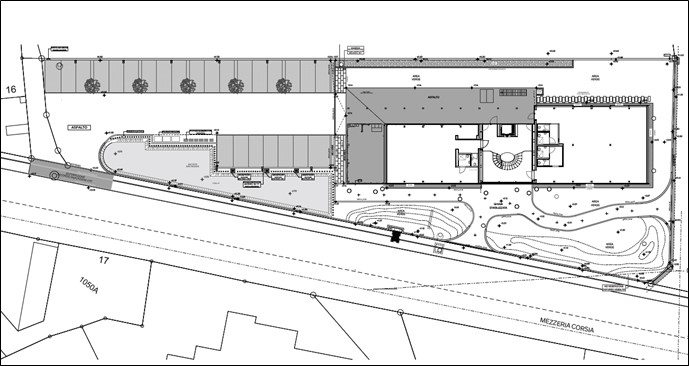
Architectural plan: level 0
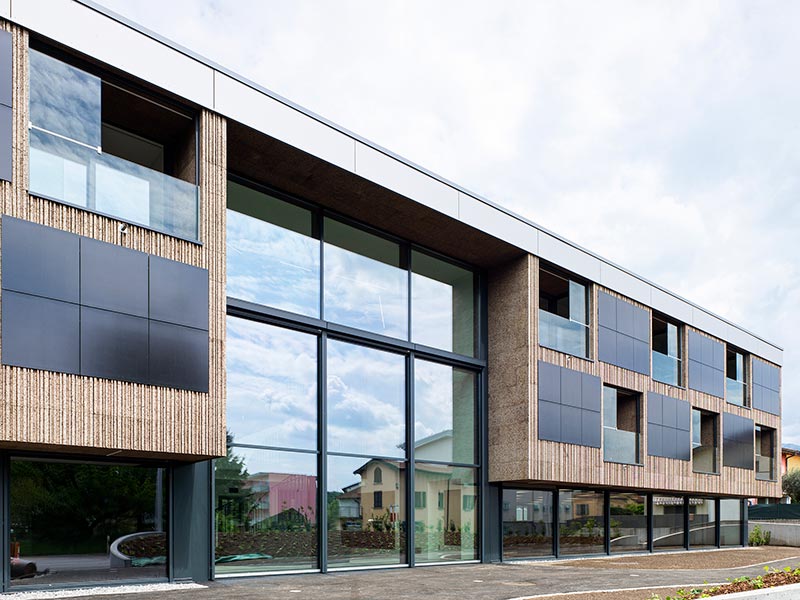

South facade
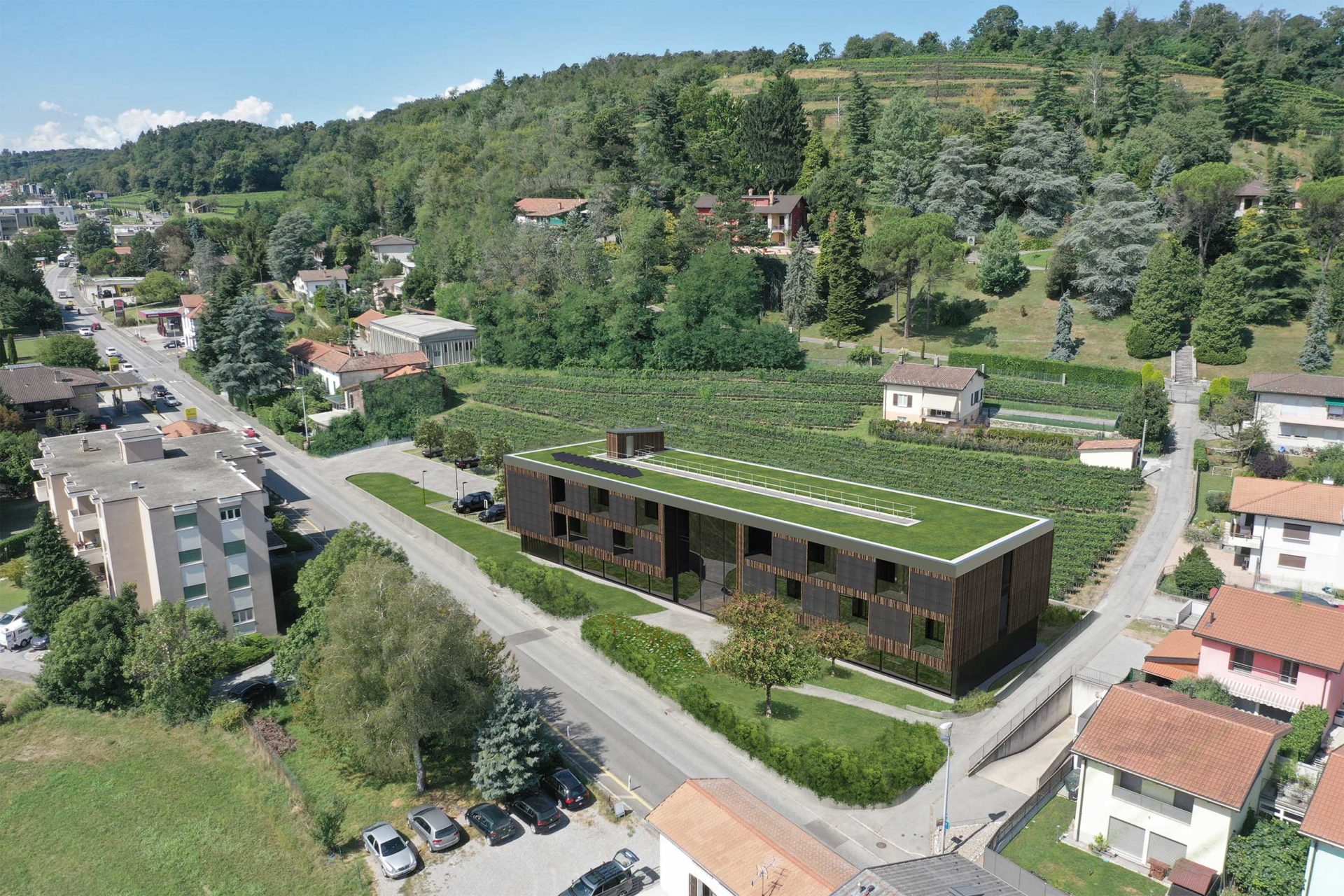

Aerial view of the building
| Active solar surface | n/a | n/a |
| Active solar surface ratio | >5% | >30% |
| Nominal power | 4.5 kWp | 22.4 kWp |
| Building skin application | Flat roof | Cladding |
| Storage | Electrical battery | n/a |
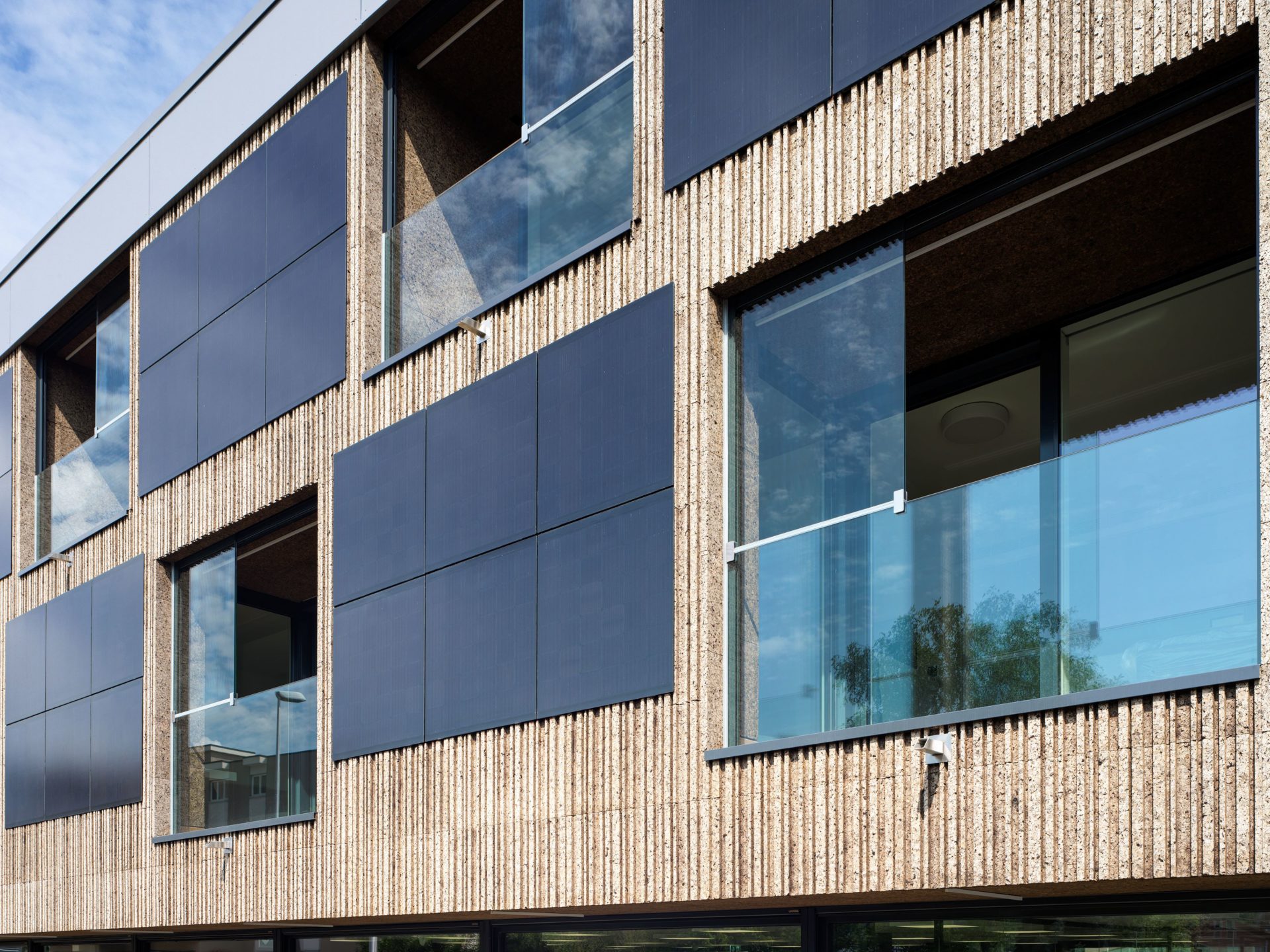

The idea of the facade is to recreate a technological cortex with a pattern reminiscent of the digital world of barcodes interspersed with photovoltaic modules, all through the use of environmentally sustainable materials.
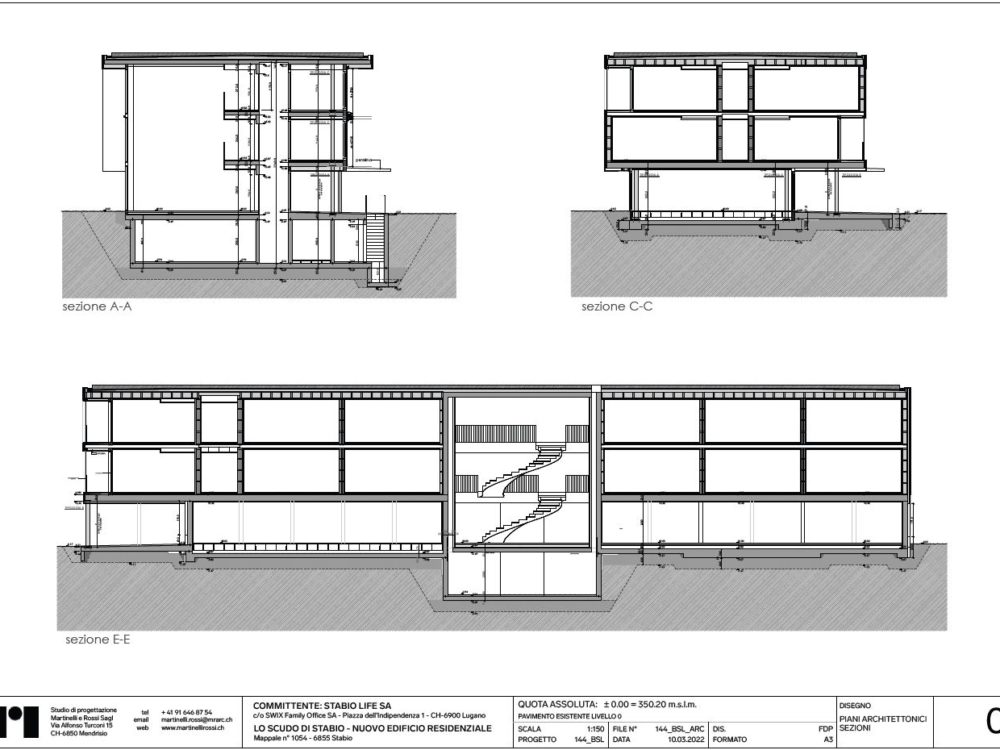
The building is designed according to timber prefabrication logic with a predominantly frame structure, with the exception of the intermediate floor slab, which is made of XLAM (cross-laminated timber).
Crystalline silicon photovoltaic modules were embedded in the south and west facades, integrating them into the exposed cork cladding through a continuous fastening system consisting of aluminium rails.
The volumetric compactness of the new building was a prerequisite for ensuring the highest energy standard.
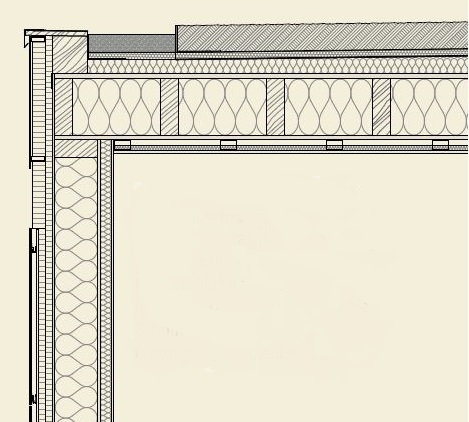
Source: Studio di Progettazione Martinelli e Rossi Sagl.
Source: Studio di Progettazione Martinelli e Rossi Sagl.