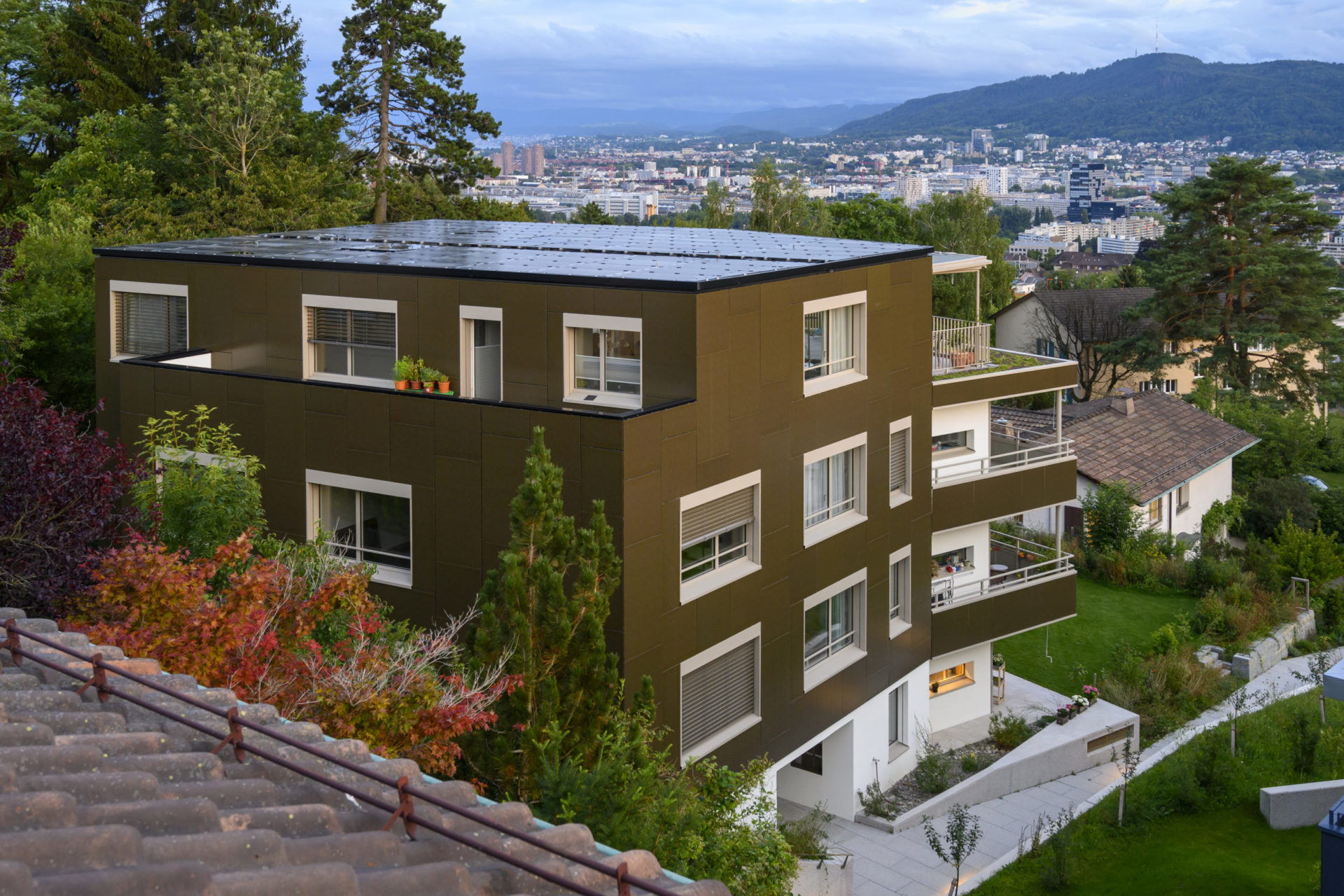
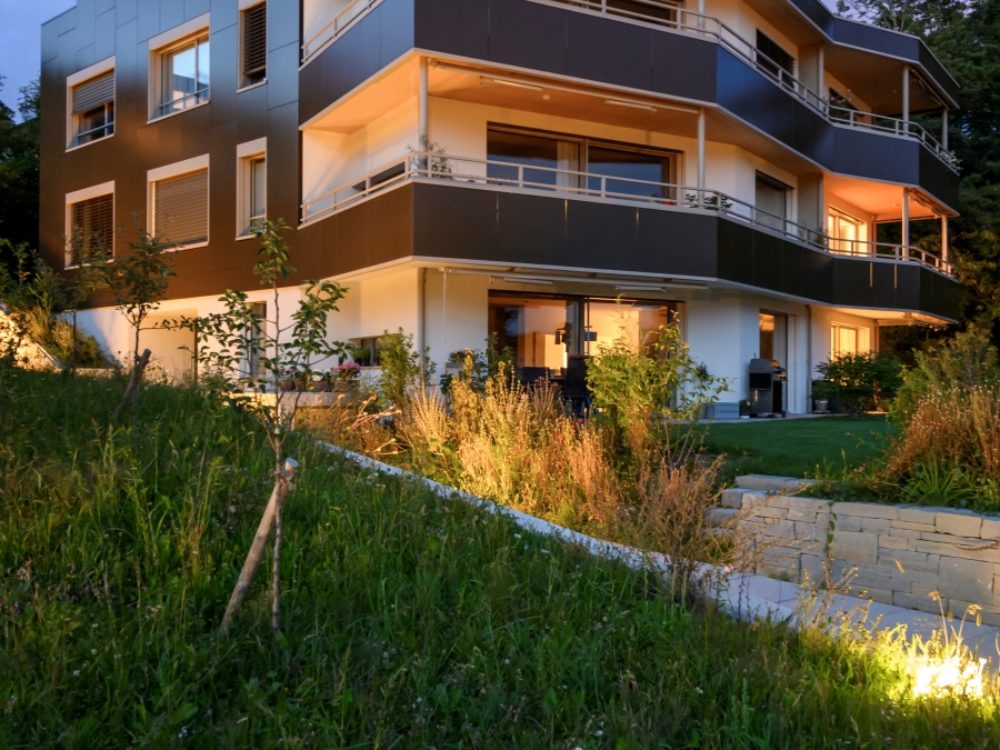
In Höngg, on the sunny slope side of Zurich, instead of a single-family house, there is now a residential building with six apartments, designed following the “Plus Energy Building (PEB)” concept. The new building has an area about two and a half times the size of the old construction, but uses only half as much energy.
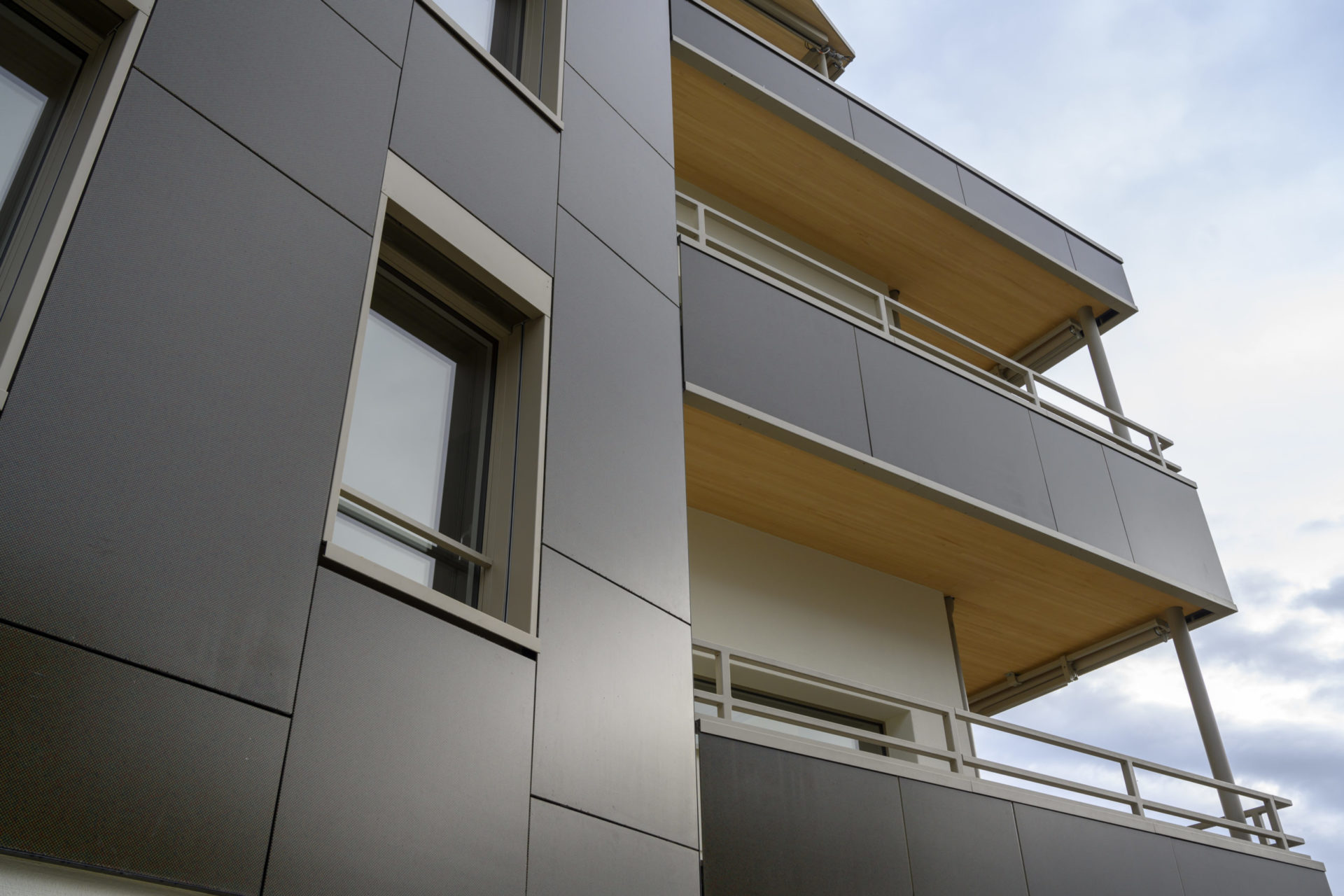
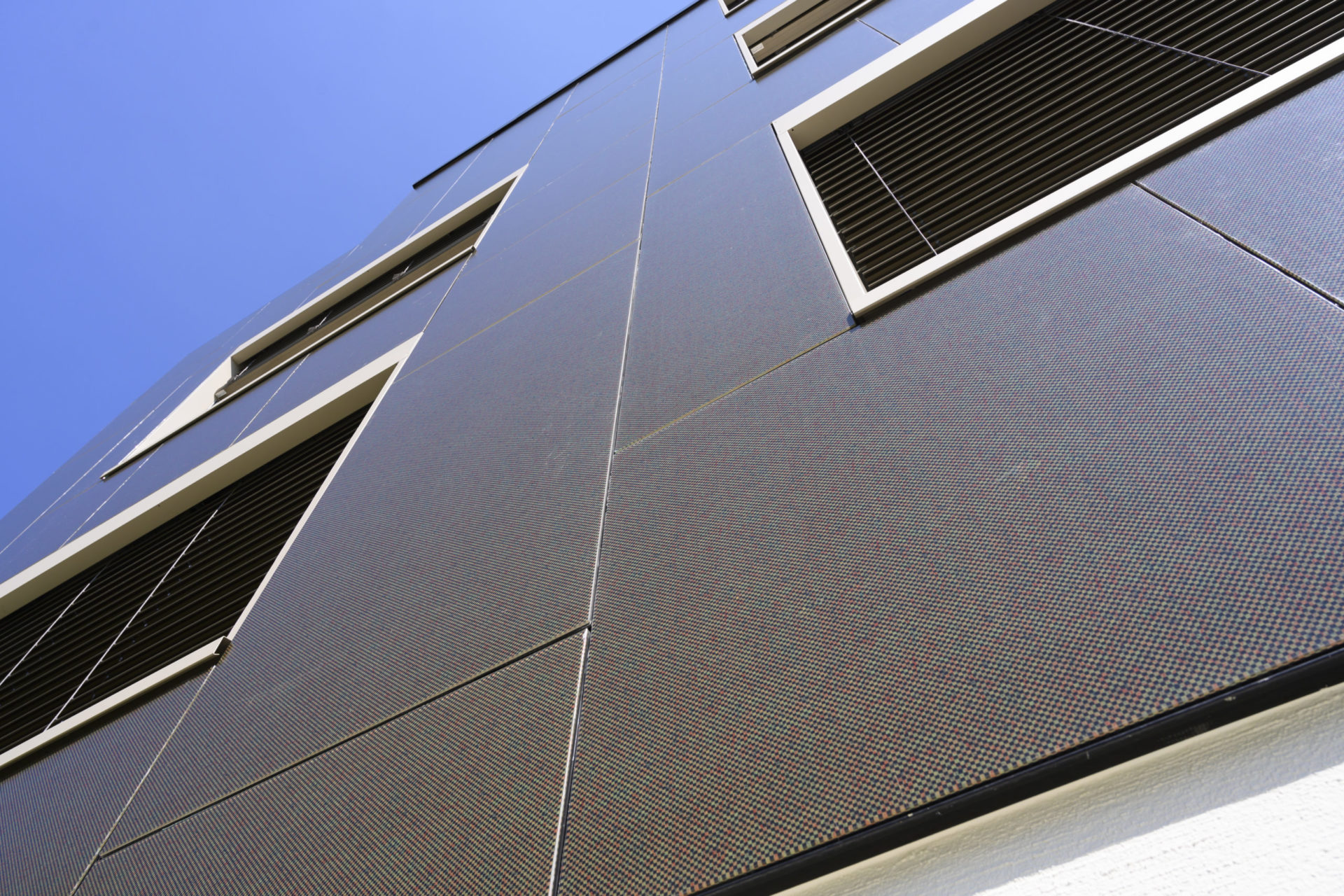
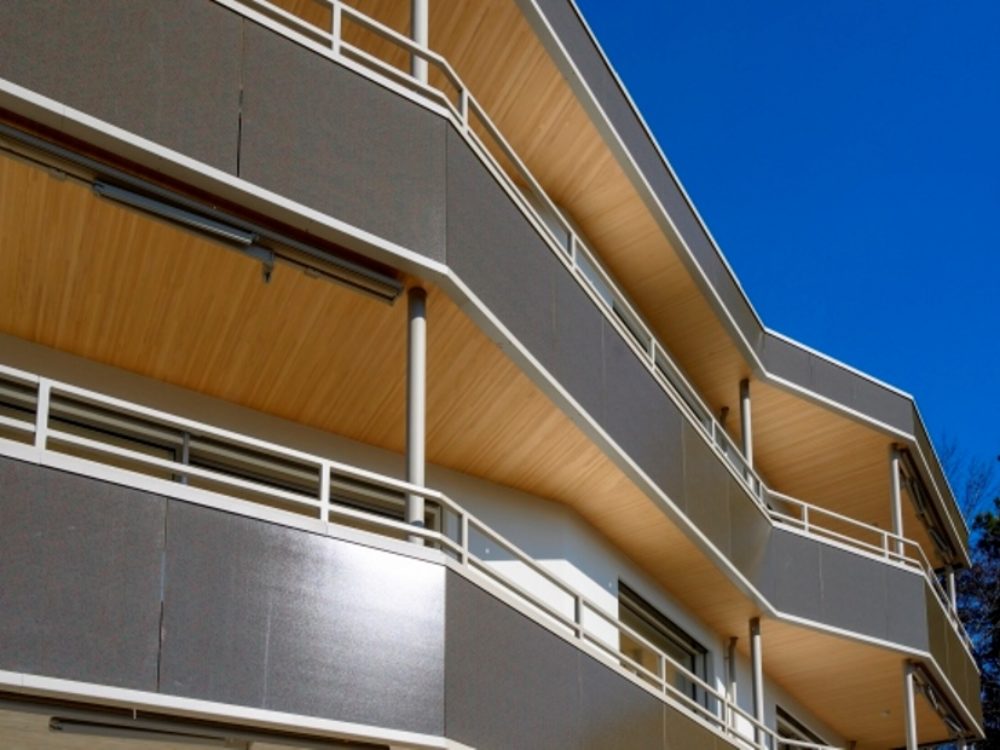
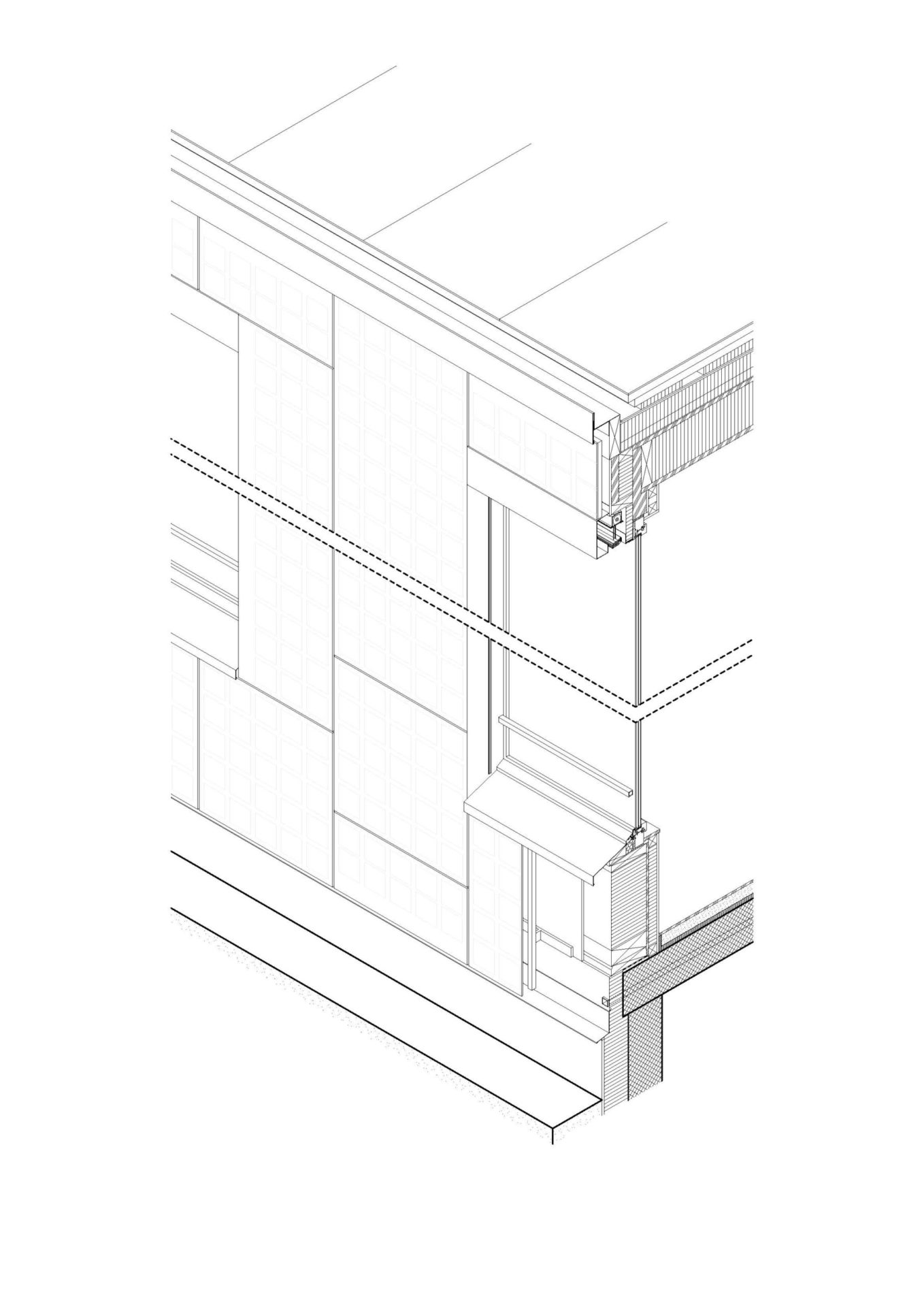
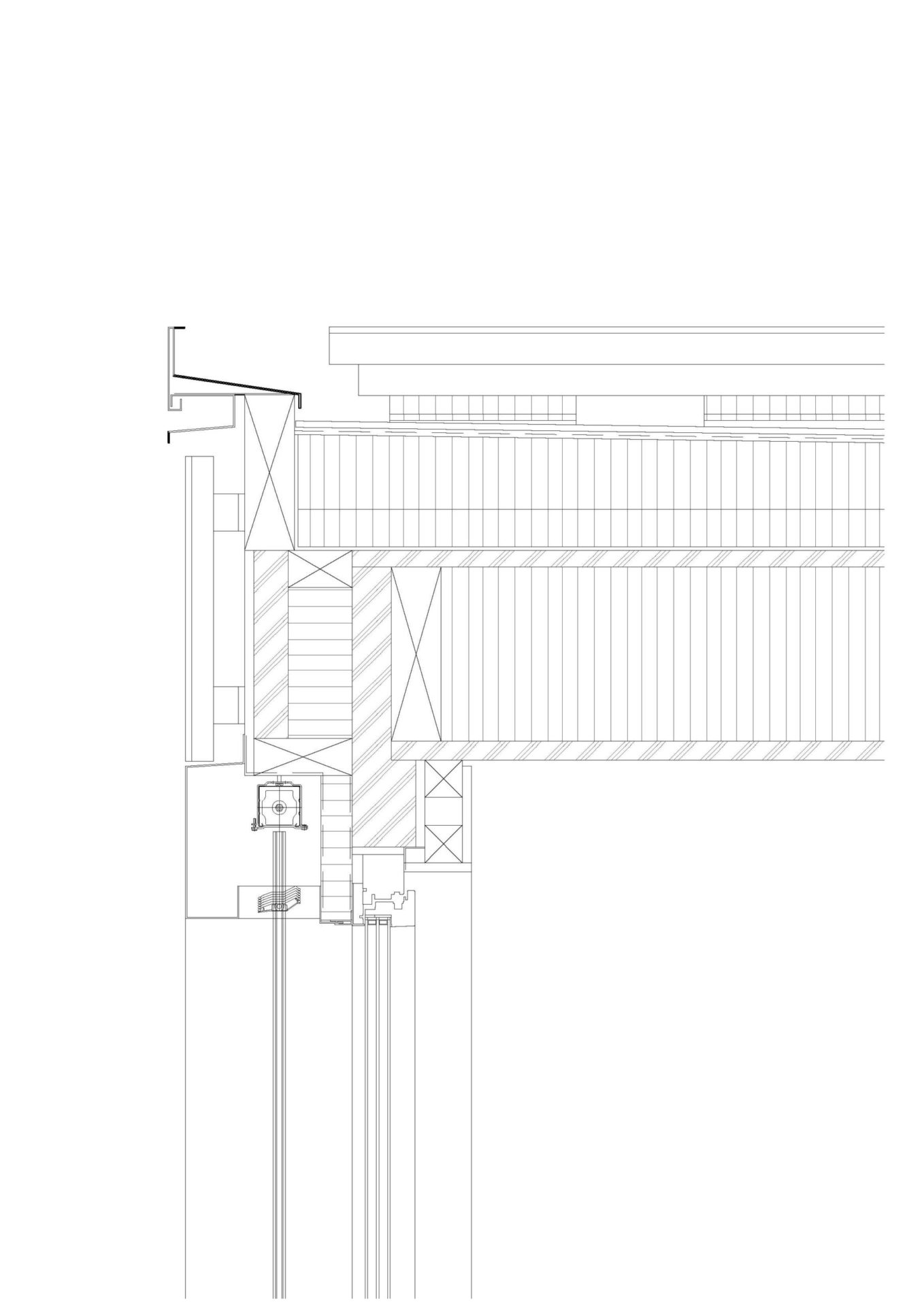
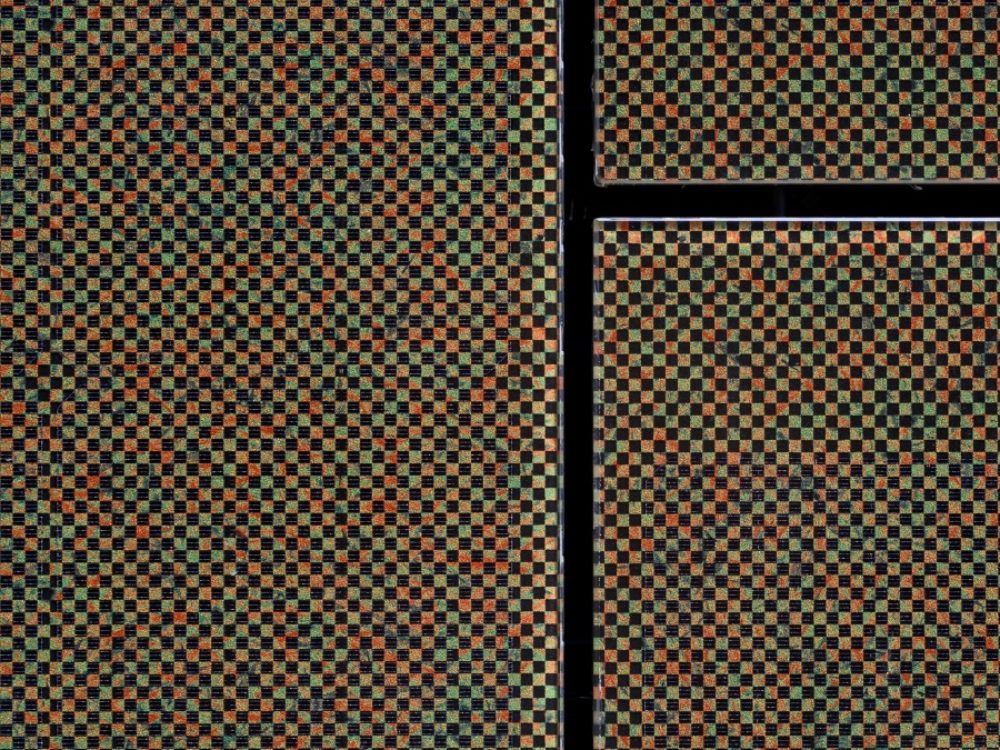
The apartment building is designed as a solar power plant. The prefabricated timber construction is optimally insulated and at the same time, the generous windows passively use solar energy. The roof and the facades are both completely clad with photovoltaic modules that produce more electricity than the house and its occupants consume. The facade installation is made with photovoltaic modules characterized by a decorative ceramic-printed modules with check patterns to avoid a “technoid” expression.

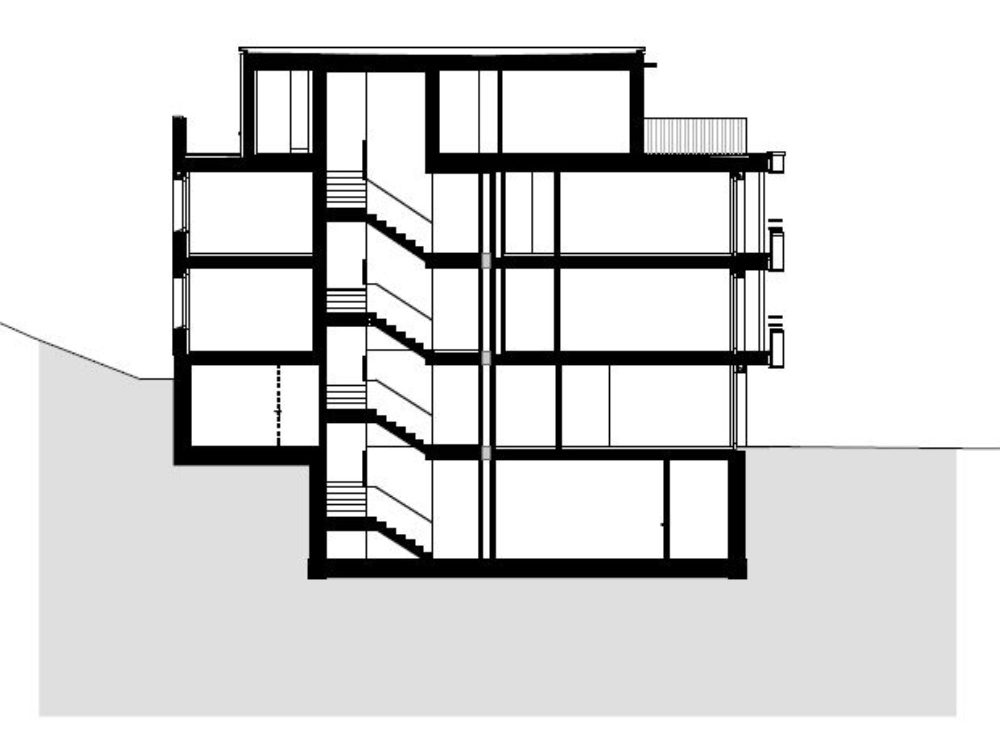
Ground floor

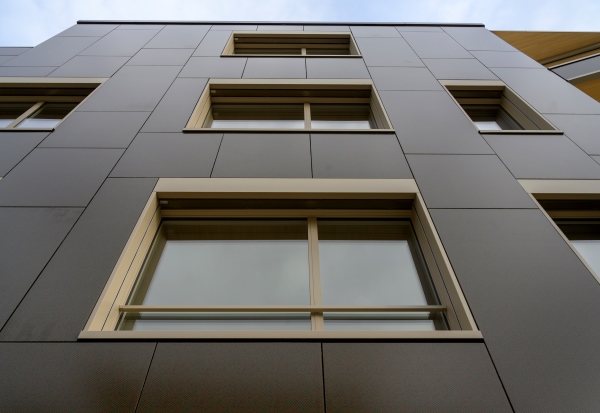
Extensive windows allow to optimize solar gains.

The building envelope is completely cladded with BIPV modules.
| Active solar surface | 141 m² | 339 m² |
| Active solar surface ratio | >75% | >75% |
| Peak power | 25.1 kWp | 42.3 kWp |
| Building skin application | Flat roof | Cold facade |
| Storage | Electric battery | 30 kWh |
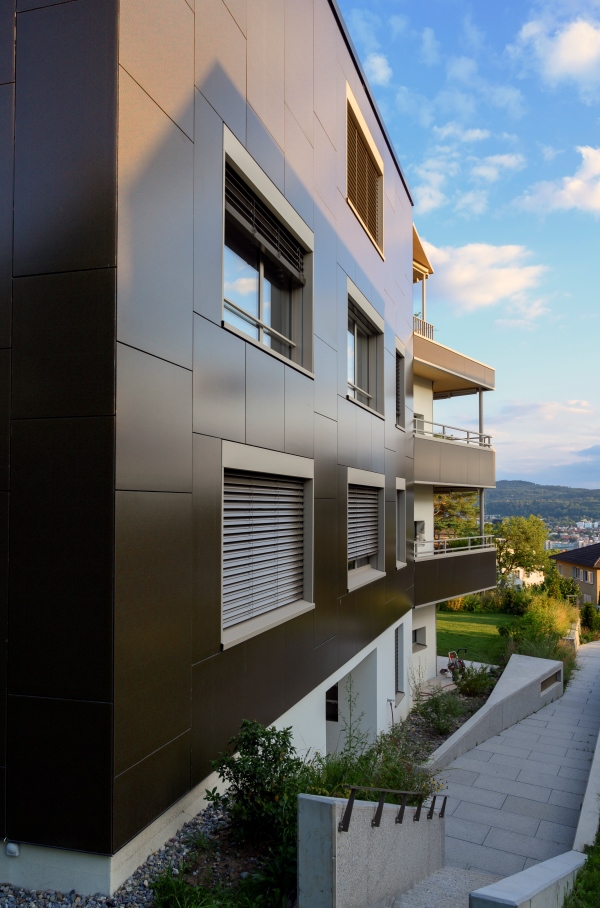

Aesthetically, the photovoltaic modules are practically indistinguishable from a standard cladding.
Already in the design stage, a grid was defined based on a multiple of the building length without remaining areas. This was also taken into account in the static system of the timber construction. The aim was to simplify and cut the costs by reducing the number of different module sizes.
The facade modules are arranged vertically in a 1 m grid. Vertically were used four module types, which result from the heights between roof, window and building base. In the balcony railing, the same modules were turned by 90°. Through the combination of various lengths can compensate the different volumes of the balconies, spacing between the modules can vary in order not to need additional formats.